2006 Isda Definitions
Isda Definitions Pdf' title='2006 Isda Definitions Pdf' />LLM Postgraduate Laws University of London International Programmes. Admiralty law. Module A LWM0. A. Admiralty jurisdiction and procedure. OIS_IFR_US.png' alt='Copy Of 2006 Isda Definitions' title='Copy Of 2006 Isda Definitions' />Interest Rate Swap Confirmation LEGAL126209741. Master Definitions and Construction Agreement and iii the Definitions. Recently someone reminded me of the ISDA master agreement, the widely used form of master contract for overthecounter derivatives transactions. It was last updated. Supplement number 52 to the 2006 ISDA Definitions published April 6, 2017 Supplement number 52 provides for the following Addition of the following. Isda Definitions' title='2006 Isda Definitions' />Study the LLM Master of Laws by distance learning. A flexible, internationally recognised postgraduate law degree from the University of London. Isda Definitions' title='2006 Isda Definitions' />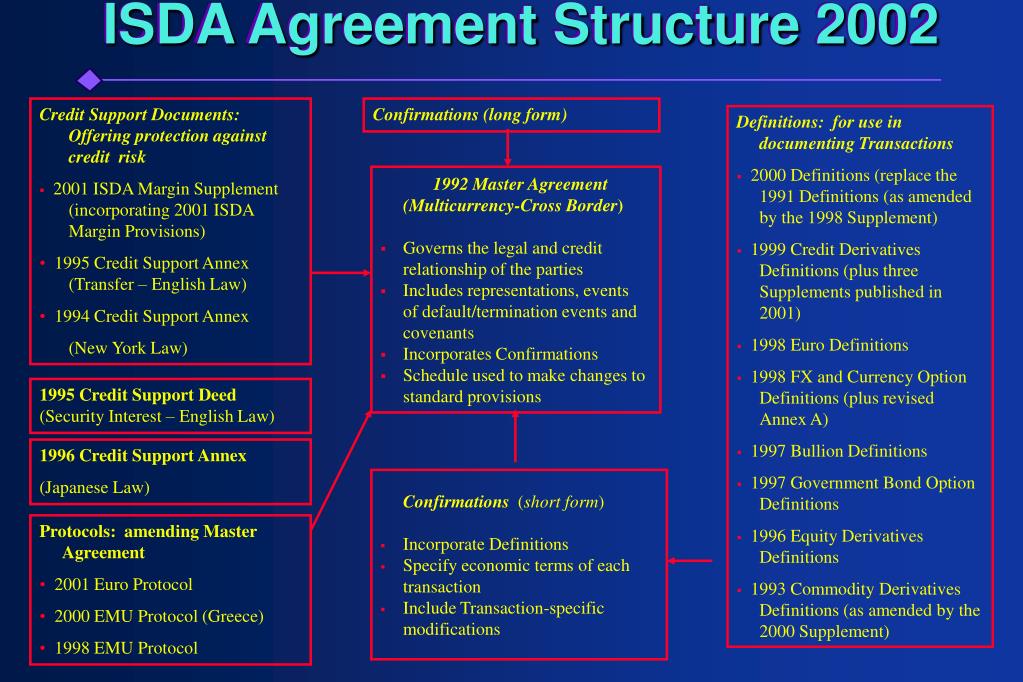 Introduction and nature of jurisdiction enforceable maritime claims. Exercise of jurisdiction, actions in rem and in personam, maritime liens and procedure. Rules and doctrines restricting the jurisdiction of the Admiralty court. Convention jurisdiction basis and multiple proceedings. Module B LWM0. 1B. Acquiring ownership in ships and the ship as property. Ownership, management and potential liabilities. Ship mortgages. Shipbuilding. Ship sale and purchase. Module C LWM0. 1C. Safety regulations in navigation, liabilities and limitation of liability. Collision regulations for conduct of vessels. Criminal liabilities for breach of statutes or breach of duty. Civil liabilities for negligence causing damage apportionment of loss and measure of damages limitation of liability. Module D LWM0. 1D. Assistance at sea and in ports. The concept of salvage under maritime law and the Salvage Conventions. Preconditions and elements of salvage salvage agreements assessment of award and special compensation. Liability of salvors for negligence and limitation. Towage contracts liabilities to third parties arising from negligence during towage. The law regulating the rights and obligations of port authorities and pilots. Sequence Module C before Module D. Textbook Aleka Mandaraka Sheppard, Modern Admiralty Law London Cavendish Publishing, 2. ISBN 1. 85. 94. 15. Applicable laws and procedures in international commercial arbitration Students wishing to study and be examined in this course are advised to successfully complete Regulation and infrastructure of international commercial arbitration in full before attempting Applicable laws and procedures in international commercial arbitration. Module A LWM0. 3A. Applicable law issues in arbitration. Determination of applicable law. Applicable substantive law. Transnational rules, lex mercatoria and trade usages. Arbitration and EU Laws. Module B LWM0. 3B. Procedure and evidence in arbitration. Law governing the arbitration procedure. Commencement of arbitration terms of reference procedural directions. Procedural issues. Taking evidence. Module C LWM0. C. Jurisdictional issues in arbitration. Arbitrability. Determination of jurisdiction. Provisional measures. Multi party and multi contract disputes. Module D LWM0. 3D. Arbitration award form, content, challenge and enforcement. Form and content. Finality and challenges to award. Recognition and enforcement. Sequence Module A first. Textbook Julian D. M. Lew, Loukas A. Mistelis and Stefan Kr. Carriage of goods by sea. Module A LWM0. 5A. Contracts of affreightment and voyage charter parties. Owners implied obligations seaworthiness, reasonable despatch and no deviation consequences for breach under common law conditions, warranties, innominate terms representations descriptions of ship, date of arrival, cancelling. Charterers obligations nomination of safe port, notification of owners of dangerous cargo. Voyage Charter parties Owners obligation as to the ship, readiness to load and cancelling clauses Charterers duty to load a full and complete cargo Loading and discharging Laytime and demurrage Freight, lien and cesser clauses. Module B LWM0. 5B. Time charter parties. Nature description of ship, delivery date and cancelling clause charter period early or late redelivery remedies arising from early or late delivery payment of hire off hire deductions from hire withdrawal of ship for no punctual payment employment and indemnity clause owners liens on freight or sub freight. Module C LWM0. 5C. The bill of lading contract and functions. The bill of lading as a contract incorporation of charter party terms identity of carrier the bill of lading and third parties. The bill of lading as a receipt representations as to quantity, condition and identity leading marks of cargo common law and statutory estoppel. The bill of lading as a document of title and the Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1. Legal functions of other types of transport document seaway bills, ships delivery orders and multimodal transport documents. Module D LWM0. 5D. International conventions regulating the rights and obligations of the parties to the bill of lading contract. The Hague and HagueVisby Rules the Hamburg Rules the Rotterdam Rules genesis of the Rules and comparison. When do these rules apply Excluded cases period covered no contracting out the carriers duties the carriers defences responsibilities of cargo owner or shipper. Freight. Time limit for making a claim limitation of liability. Sequence Students are required to attempt the modules in order. Textbooks Wilson, J. F. Carriage of goods by sea. Harlow Longman, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 14. 08. Supplied as an e book. Dockray, M. Cases and materials on the carriage of goods by sea. Abingdon Routledge, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 11. 38. Supplied as an e book. Commercial banking law bank customer relationship. Module A LWM7. 2A. Banks and customers. What is a bank and who is a bank customerThe contract obligations of parties, significance of the mandate, termination of the contract, variation, proper law of the contract. Duty of confidentiality owed by a bank to its customers and the circumstances in which the duty can, or must, be breached. Module B LWM7. 2B. Duty of care, fiduciary duty, constructive trust and undue influence. A banks duty of care application and scope of duty. Fiduciary obligations when does bank become a fiduciary and how can it limit or exclude its obligations Constructive trust when does liability as a constructive trustee arise Undue influence types of undue influence, how can a bank protect its transactions from challenge on the grounds of undue influenceConstructive trust when does liability as a constructive trustee arise Customers duty of care. Module C LWM7. 2C. Accounts, money, payment and fund transfers. What is money, how is its transfer conceptualised legallyChattel and bank money. What is payment and how is it made Credit and debit transfers. Clearing and settlement systems. Legal relationships. Accounts and dispute resolution Accounts types of accounts and their implications Dealing with complaints Banking Codes, Financial Services Ombudsman Service. Module D LWM7. 2D. Cheques and payment cards. Cheques. What is a cheque, the obligations of, and defences available to, paying and collecting banks. Payment cards and recovering mistaken payments Payment cards debit cards, credit cards, charge cards, digital cash cards, etc. Contractual relationships Consumer Credit Act Recovering mistaken payments. Sequence Students are required to attempt the modules in order. Textbooks E. P. Ellinger, Eva Lomnicker and Richard Hooley, Ellingers Modern Banking Law 4th ed Oxford Oxford University Press, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 01. 99. Commercial trusts law. Module A LWM0. 6A. The nature of commercial trusts. Equity, trusts and commercial expectations. Jocuri Pc Copii 4 Ani. The contractarian account of trusts. Unit trusts and other financial uses of trusts. The constitution of express trusts in commercial transactions. Module B LWM0. 6B. Equitable devices used to take security in commercial contracts. Taking security in loan contracts. Equitable charges. Establishing title at common law and in equity. Example collateralisation in financial transactions. Module C LWM0. 6C. The 2. 00. 2 ISDA Master Agreement Isnt a Contract Drafting Masterpiece. Recently someone reminded me of the ISDA master agreement, the widely used form of master contract for over the counter derivatives transactions. It was last updated in 2. I found a copy of the 2. I had a look at it. My conclusion The drafting is pretty ragged. No surprise thereIve looked at a few examples of model contract language promulgated by trade groups, and theyve all been varying degrees of not so great, no matter how widely used. For example, go here for my take on the American Arbitration Associations standard arbitration clause. So below are a few comments based on my cursory review of the first four pages of the master agreement, out of 2. These comments just scratch the surface. For my analysis of another usage employed in the ISDA master agreement, see this post. Categories of Contract Language. The word will is sometimes used where Id use the simple present The terms defined in Section 1. Master Agreement will have the meanings therein specified for the purpose of this Master Agreement. The first subsection of section 2 Obligations is given the subheading General Conditions. But the first two provisions under it are obligations, so that isnt a helpful subheading. Amounts are referred to as being payable. When considered in isolation, its not clear whether the party in question has discretion to pay those amounts or is obligated to pay them. See section 2c for an example of awkward use of the passive voice instead of The election may be made, Id say The parties may so elect Defined Terms. For purposes of integrated definitions, in the 2. For example, see the three defined term parentheticals in the first sentence of the introductory clause have entered andor anticipate entering into one or more transactions each a Transaction that are or will be governed by this 2. Master Agreement, which includes the schedule the Schedule, and the documents and other confirming evidence each a Confirmation exchanged between the parties or otherwise effective for the purpose of confirming or evidencing those Transactions. Heres the next sentence in the introductory clause This 2. Master Agreement and the Schedule are together referred to as this Master Agreement. Its redundant, as is the defined term Master Agreement, in that the previous sentence specifies that the master agreement includes the schedule. The reference in the introductory clause to those Transactions is illogicalthere arent any other Transactions. Id delete the word those. In section 2c, the defined term Multiple Transaction Payment Netting is created by means of neither an integrated definition nor an autonomous definition. Thats unorthodox. Structure. Section 3 says that specified representations will be deemed to be repeated by each party on each date on which a Transaction is entered into and, in the case of the representations in Section 3f, at all times until the termination of this Agreement. I like this use of will be deemed, which matches exactly use of that phrase in the representations lead in that I recommend in The Structure of M A Contracts. But saying that a representation will be repeated at all times is very odd. Layout. The layout is based on a bastard hybrid of hanging indents and first line indents. Section 2c features dangling text and an unenumerated paragraph, both MSCD no nos. In section 2d, a separate sentence, with its own set of tabulated enumerated clauses, it tacked on to the last of a set of tabulated enumerated clauses. Instead, the period at the end of the last of a set of tabulated enumerated clauses should be followed only by a new section or subsection. Drafting As Writing. The andor in the introductory clause entered andor anticipate entering into isnt great. Dont beat about the bush. Heres the current section 1c All Transactions are entered into in reliance on the fact that this Master Agreement and all Confirmations form a single agreement between the parties collectively referred to as this Agreement, and the parties would not otherwise enter into any Transactions. Heres my version limiting my changes This Master Agreement and all Confirmations form a single agreement between the parties collectively referred to as this Agreement. Such is used instead of this, that, these, and those. Thats a hallmark of needlessly legalistic prose. Abstract nouns bad, verbs good. For example, see section 2b by giving notice to read notifying the other party Section 2dii contains the following if Y has failed to comply with or perform any agreement contained in Section 4ai, 4aiii or 4d. Id say if Y has failed to comply with section 4ai, 4aiii or 4d. Why both comply with and perform And why refer to as an agreement an obligation contained within a given provision Section 3a uses the subheading Basic Representations. Its unhelpful to offer opinions regarding the complexity of, or importance of, a set of provisions. Section 3e and 3f refer to representations as being accurate and true. Im sympathetic to use of complete and accurate, but not accurate and true. Id use just accurate.
Introduction and nature of jurisdiction enforceable maritime claims. Exercise of jurisdiction, actions in rem and in personam, maritime liens and procedure. Rules and doctrines restricting the jurisdiction of the Admiralty court. Convention jurisdiction basis and multiple proceedings. Module B LWM0. 1B. Acquiring ownership in ships and the ship as property. Ownership, management and potential liabilities. Ship mortgages. Shipbuilding. Ship sale and purchase. Module C LWM0. 1C. Safety regulations in navigation, liabilities and limitation of liability. Collision regulations for conduct of vessels. Criminal liabilities for breach of statutes or breach of duty. Civil liabilities for negligence causing damage apportionment of loss and measure of damages limitation of liability. Module D LWM0. 1D. Assistance at sea and in ports. The concept of salvage under maritime law and the Salvage Conventions. Preconditions and elements of salvage salvage agreements assessment of award and special compensation. Liability of salvors for negligence and limitation. Towage contracts liabilities to third parties arising from negligence during towage. The law regulating the rights and obligations of port authorities and pilots. Sequence Module C before Module D. Textbook Aleka Mandaraka Sheppard, Modern Admiralty Law London Cavendish Publishing, 2. ISBN 1. 85. 94. 15. Applicable laws and procedures in international commercial arbitration Students wishing to study and be examined in this course are advised to successfully complete Regulation and infrastructure of international commercial arbitration in full before attempting Applicable laws and procedures in international commercial arbitration. Module A LWM0. 3A. Applicable law issues in arbitration. Determination of applicable law. Applicable substantive law. Transnational rules, lex mercatoria and trade usages. Arbitration and EU Laws. Module B LWM0. 3B. Procedure and evidence in arbitration. Law governing the arbitration procedure. Commencement of arbitration terms of reference procedural directions. Procedural issues. Taking evidence. Module C LWM0. C. Jurisdictional issues in arbitration. Arbitrability. Determination of jurisdiction. Provisional measures. Multi party and multi contract disputes. Module D LWM0. 3D. Arbitration award form, content, challenge and enforcement. Form and content. Finality and challenges to award. Recognition and enforcement. Sequence Module A first. Textbook Julian D. M. Lew, Loukas A. Mistelis and Stefan Kr. Carriage of goods by sea. Module A LWM0. 5A. Contracts of affreightment and voyage charter parties. Owners implied obligations seaworthiness, reasonable despatch and no deviation consequences for breach under common law conditions, warranties, innominate terms representations descriptions of ship, date of arrival, cancelling. Charterers obligations nomination of safe port, notification of owners of dangerous cargo. Voyage Charter parties Owners obligation as to the ship, readiness to load and cancelling clauses Charterers duty to load a full and complete cargo Loading and discharging Laytime and demurrage Freight, lien and cesser clauses. Module B LWM0. 5B. Time charter parties. Nature description of ship, delivery date and cancelling clause charter period early or late redelivery remedies arising from early or late delivery payment of hire off hire deductions from hire withdrawal of ship for no punctual payment employment and indemnity clause owners liens on freight or sub freight. Module C LWM0. 5C. The bill of lading contract and functions. The bill of lading as a contract incorporation of charter party terms identity of carrier the bill of lading and third parties. The bill of lading as a receipt representations as to quantity, condition and identity leading marks of cargo common law and statutory estoppel. The bill of lading as a document of title and the Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1. Legal functions of other types of transport document seaway bills, ships delivery orders and multimodal transport documents. Module D LWM0. 5D. International conventions regulating the rights and obligations of the parties to the bill of lading contract. The Hague and HagueVisby Rules the Hamburg Rules the Rotterdam Rules genesis of the Rules and comparison. When do these rules apply Excluded cases period covered no contracting out the carriers duties the carriers defences responsibilities of cargo owner or shipper. Freight. Time limit for making a claim limitation of liability. Sequence Students are required to attempt the modules in order. Textbooks Wilson, J. F. Carriage of goods by sea. Harlow Longman, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 14. 08. Supplied as an e book. Dockray, M. Cases and materials on the carriage of goods by sea. Abingdon Routledge, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 11. 38. Supplied as an e book. Commercial banking law bank customer relationship. Module A LWM7. 2A. Banks and customers. What is a bank and who is a bank customerThe contract obligations of parties, significance of the mandate, termination of the contract, variation, proper law of the contract. Duty of confidentiality owed by a bank to its customers and the circumstances in which the duty can, or must, be breached. Module B LWM7. 2B. Duty of care, fiduciary duty, constructive trust and undue influence. A banks duty of care application and scope of duty. Fiduciary obligations when does bank become a fiduciary and how can it limit or exclude its obligations Constructive trust when does liability as a constructive trustee arise Undue influence types of undue influence, how can a bank protect its transactions from challenge on the grounds of undue influenceConstructive trust when does liability as a constructive trustee arise Customers duty of care. Module C LWM7. 2C. Accounts, money, payment and fund transfers. What is money, how is its transfer conceptualised legallyChattel and bank money. What is payment and how is it made Credit and debit transfers. Clearing and settlement systems. Legal relationships. Accounts and dispute resolution Accounts types of accounts and their implications Dealing with complaints Banking Codes, Financial Services Ombudsman Service. Module D LWM7. 2D. Cheques and payment cards. Cheques. What is a cheque, the obligations of, and defences available to, paying and collecting banks. Payment cards and recovering mistaken payments Payment cards debit cards, credit cards, charge cards, digital cash cards, etc. Contractual relationships Consumer Credit Act Recovering mistaken payments. Sequence Students are required to attempt the modules in order. Textbooks E. P. Ellinger, Eva Lomnicker and Richard Hooley, Ellingers Modern Banking Law 4th ed Oxford Oxford University Press, 2. ISBN 9. 78. 01. 99. Commercial trusts law. Module A LWM0. 6A. The nature of commercial trusts. Equity, trusts and commercial expectations. Jocuri Pc Copii 4 Ani. The contractarian account of trusts. Unit trusts and other financial uses of trusts. The constitution of express trusts in commercial transactions. Module B LWM0. 6B. Equitable devices used to take security in commercial contracts. Taking security in loan contracts. Equitable charges. Establishing title at common law and in equity. Example collateralisation in financial transactions. Module C LWM0. 6C. The 2. 00. 2 ISDA Master Agreement Isnt a Contract Drafting Masterpiece. Recently someone reminded me of the ISDA master agreement, the widely used form of master contract for over the counter derivatives transactions. It was last updated in 2. I found a copy of the 2. I had a look at it. My conclusion The drafting is pretty ragged. No surprise thereIve looked at a few examples of model contract language promulgated by trade groups, and theyve all been varying degrees of not so great, no matter how widely used. For example, go here for my take on the American Arbitration Associations standard arbitration clause. So below are a few comments based on my cursory review of the first four pages of the master agreement, out of 2. These comments just scratch the surface. For my analysis of another usage employed in the ISDA master agreement, see this post. Categories of Contract Language. The word will is sometimes used where Id use the simple present The terms defined in Section 1. Master Agreement will have the meanings therein specified for the purpose of this Master Agreement. The first subsection of section 2 Obligations is given the subheading General Conditions. But the first two provisions under it are obligations, so that isnt a helpful subheading. Amounts are referred to as being payable. When considered in isolation, its not clear whether the party in question has discretion to pay those amounts or is obligated to pay them. See section 2c for an example of awkward use of the passive voice instead of The election may be made, Id say The parties may so elect Defined Terms. For purposes of integrated definitions, in the 2. For example, see the three defined term parentheticals in the first sentence of the introductory clause have entered andor anticipate entering into one or more transactions each a Transaction that are or will be governed by this 2. Master Agreement, which includes the schedule the Schedule, and the documents and other confirming evidence each a Confirmation exchanged between the parties or otherwise effective for the purpose of confirming or evidencing those Transactions. Heres the next sentence in the introductory clause This 2. Master Agreement and the Schedule are together referred to as this Master Agreement. Its redundant, as is the defined term Master Agreement, in that the previous sentence specifies that the master agreement includes the schedule. The reference in the introductory clause to those Transactions is illogicalthere arent any other Transactions. Id delete the word those. In section 2c, the defined term Multiple Transaction Payment Netting is created by means of neither an integrated definition nor an autonomous definition. Thats unorthodox. Structure. Section 3 says that specified representations will be deemed to be repeated by each party on each date on which a Transaction is entered into and, in the case of the representations in Section 3f, at all times until the termination of this Agreement. I like this use of will be deemed, which matches exactly use of that phrase in the representations lead in that I recommend in The Structure of M A Contracts. But saying that a representation will be repeated at all times is very odd. Layout. The layout is based on a bastard hybrid of hanging indents and first line indents. Section 2c features dangling text and an unenumerated paragraph, both MSCD no nos. In section 2d, a separate sentence, with its own set of tabulated enumerated clauses, it tacked on to the last of a set of tabulated enumerated clauses. Instead, the period at the end of the last of a set of tabulated enumerated clauses should be followed only by a new section or subsection. Drafting As Writing. The andor in the introductory clause entered andor anticipate entering into isnt great. Dont beat about the bush. Heres the current section 1c All Transactions are entered into in reliance on the fact that this Master Agreement and all Confirmations form a single agreement between the parties collectively referred to as this Agreement, and the parties would not otherwise enter into any Transactions. Heres my version limiting my changes This Master Agreement and all Confirmations form a single agreement between the parties collectively referred to as this Agreement. Such is used instead of this, that, these, and those. Thats a hallmark of needlessly legalistic prose. Abstract nouns bad, verbs good. For example, see section 2b by giving notice to read notifying the other party Section 2dii contains the following if Y has failed to comply with or perform any agreement contained in Section 4ai, 4aiii or 4d. Id say if Y has failed to comply with section 4ai, 4aiii or 4d. Why both comply with and perform And why refer to as an agreement an obligation contained within a given provision Section 3a uses the subheading Basic Representations. Its unhelpful to offer opinions regarding the complexity of, or importance of, a set of provisions. Section 3e and 3f refer to representations as being accurate and true. Im sympathetic to use of complete and accurate, but not accurate and true. Id use just accurate.